Documentation: Switch Conditional Node¶
Overview¶
The Switch Conditional Node evaluates cases in order and exits through the connector of the first case whose condition is met. You can define a default case when none match. Unlike the IF node (which only has true and false routes), the Switch supports multiple outputs, one per case or connector defined.
When to Use This Node¶
Use this node when you need to:
- Route the flow based on the value of a variable (e.g.,
"yes"→ branch A,"no"→ branch B) - Have multiple branches instead of just true/false
- Define a default case for any value not covered
- Evaluate the same expression against several possible values (like a
switchin programming)
Connectors (outputs)¶
- Per case: each case defines a
connector(string). The engine follows the connection whose connector matches the value returned by the node. - No match: if no case matches and there is no default case, the node returns the
falseconnector. - Error fallback: if the node fails during execution, the flow can continue through the
falseconnector.
Node Configuration¶
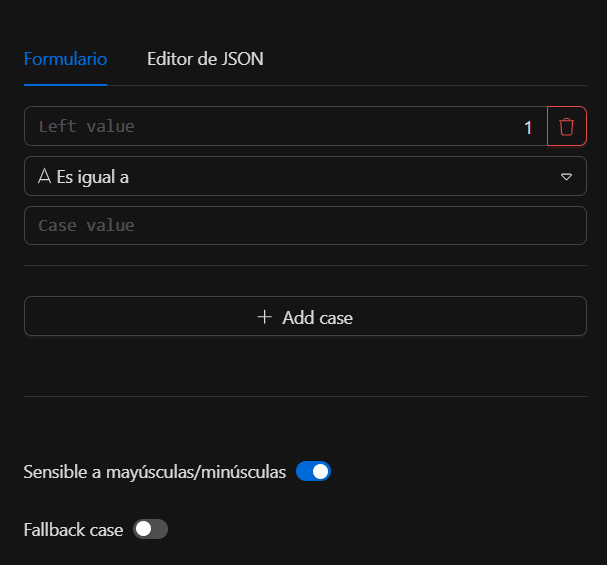
Step 1: Add cases (required)¶
The cases field is a required array with at least one element. Each case is an object with:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
leftValue |
any | Yes* | Left-hand value for the comparison (e.g., variable from context). |
operator |
object | Yes* | Operator (type + operation). See supported operations below. |
rightValue |
any | Per op. | Right-hand value. Not used in "single value" operations. |
isDefault |
bool | No | If true, this is the default case (used when no other case matches). |
connector |
string | Yes | Connector through which the flow exits when this case matches (or is default). |
* For the default case (isDefault: true), operator may be empty; the condition is not evaluated.
Step 2: Options (optional)¶
In options you can configure:
caseSensitive(bool): iffalse, forstringoperatorsleftValueandrightValueare lowercased before comparison.
Operator (SwitchOperator)¶
Each case includes an operator object with:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
string | Label (e.g., "equals"); does not affect logic. |
operation |
string | Operation code (see tables below). |
singleValue |
bool | If true (only for type number), rightValue is not used (exists/empty). |
type |
string | string, number, boolean, or array. |
Warning
Types object, null, and undefined are not implemented; they return error "unsupported operator type".
Supported operations¶
Type string¶
| Operation | Code | rightValue | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exists | exists |
No | leftValue != "" |
| Does not exist | does not exist |
No | leftValue == "" |
| Is empty | is empty |
No | leftValue == "" |
| Is not empty | is not empty |
No | leftValue != "" |
| Equal to | is equal to |
Yes | Equality (subject to caseSensitive). |
| Not equal to | is not equal to |
Yes | Inequality. |
| Contains | contains |
Yes | Substring. |
| Does not contain | does not contain |
Yes | Negation of contains. |
| Starts with | starts with |
Yes | Prefix. |
| Does not start with | does not start with |
Yes | Negation. |
| Ends with | ends with |
Yes | Suffix. |
| Does not end with | does not end with |
Yes | Negation. |
| Matches regex | matches regex |
Yes | rightValue = regex pattern. |
| Does not match regex | does not match regex |
Yes | Negation. |
| Greater than | is greater than |
Yes | Lexicographic comparison. |
| Less than | is less than |
Yes | Lexicographic comparison. |
| Greater or equal | is greater than or equal to |
Yes | Lexicographic comparison. |
| Less or equal | is less than or equal to |
Yes | Lexicographic comparison. |
Note
For type string, "greater/less" comparisons are lexicographic, not numeric. Use type number for numeric comparisons.
Type number¶
With singleValue: true (rightValue not used):
| Operation | Code |
|---|---|
| Exists | exists |
| Does not exist | does not exist |
| Is empty | is empty |
| Is not empty | is not empty |
With singleValue: false (leftValue and rightValue converted to number):
| Operation | Code |
|---|---|
| Equal to | is equal to |
| Not equal to | is not equal to |
| Greater than | is greater than |
| Less than | is less than |
| Greater or equal | is greater than or equal to |
| Less or equal | is less than or equal to |
Type boolean¶
| Operation | Code |
|---|---|
| Equal to | is equal to |
| Not equal to | is not equal to |
leftValue and rightValue must be booleans; otherwise the case returns an error.
Type array¶
| Operation | Code | rightValue | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contains | contains |
Any value | Array contains an equal element (DeepEqual). |
| Equal to | is equal to |
Array | Deep equality of arrays. |
| Is empty | is empty |
No | len(leftValue) == 0 |
| Is not empty | is not empty |
No | len(leftValue) > 0 |
leftValue must be an array; otherwise the case returns an error.
Evaluation order¶
casesare traversed in the order defined.- The case with
isDefault: trueis ignored for evaluation (used only as fallback). - For each non-default case, leftValue operator rightValue is evaluated.
- First case that returns true: evaluation stops and that case’s
connectoris returned. - If none match and there is a case with
isDefault: true, the default case’sconnectoris returned. - If there is no match and no default, the
falseconnector is returned.
JSON structure¶
Example node configuration:
{
"cases": [
{
"connector": "67b6297a10f",
"isDefault": false,
"leftValue": "{{node6bdb5c4975e.response.danger}}",
"operator": {
"name": "is equal to",
"operation": "is equal to",
"singleValue": true,
"type": "string"
},
"rightValue": "no"
},
{
"connector": "df2efe7863f",
"isDefault": false,
"leftValue": "{{node6bdb5c4975e.response.danger}}",
"operator": {
"name": "is equal to",
"operation": "is equal to",
"singleValue": true,
"type": "string"
},
"rightValue": "yes"
}
],
"options": {
"caseSensitive": true
}
}
Example with default case¶
{
"options": { "caseSensitive": false },
"cases": [
{
"leftValue": "{{trigger.status}}",
"operator": {
"name": "equals",
"operation": "is equal to",
"singleValue": false,
"type": "string"
},
"rightValue": "active",
"connector": "active_branch"
},
{
"leftValue": "{{trigger.status}}",
"operator": {
"name": "equals",
"operation": "is equal to",
"singleValue": false,
"type": "string"
},
"rightValue": "inactive",
"connector": "inactive_branch"
},
{
"leftValue": "",
"operator": {},
"isDefault": true,
"connector": "default_branch"
}
]
}
Graph connections must use as connector the values defined in each case (active_branch, inactive_branch, default_branch, etc.) according to the branches you configured.
Usage examples¶
Example 1: Route by "yes" / "no" response¶
Use case: based on a previous node’s danger field, follow one branch or another.
danger="yes"→ connector of the first case matching"yes".danger="no"→ connector of the case matching"no".- Other value → connector
false(or add a case withisDefault: true).
Configuration: two cases with operator.type = "string", operation = "is equal to", and rightValue "yes" and "no" respectively, each with its own connector.
Example 2: Multiple states with default¶
Use case: trigger status active, inactive, or any other.
- Three cases: two with
rightValue"active"and"inactive"and their connectors; the third withisDefault: trueand"connector": "default_branch".
Troubleshooting¶
Error: "unsupported operator type"¶
Cause: operator.type is object, null, undefined, or an unsupported type.
Fix: use only string, number, boolean, or array.
No case matches and no default¶
Behavior: the node returns the false connector. Connect that output in the graph if you want to handle the "no match" case.
Default case is not used¶
Cause: the default case must have isDefault: true. If another case matches first, the default is not evaluated.
Fix: check the order of cases and that only one case has isDefault: true.
Best practices¶
- Use a default case when there may be values not covered by other cases.
- For real numeric comparisons, use
operator.type = "number"withsingleValue = false. leftValueandrightValuecan use templating (e.g.,{{node_key.output_field}}); the engine substitutes them before execution.- Keep case order aligned with the desired priority; the first matching case determines the output.