Architecture Overview¶
Netsocs Synergy is built on a modern software architecture, organized in logical layers and orchestrated by Kubernetes.
This design ensures scalability, high availability, and flexibility, allowing the platform to adapt to any environment, from small implementations to large-scale enterprise deployments.
INFO
This section is aimed at system administrators, DevOps personnel, and developers interested in understanding the internal workings of the platform.
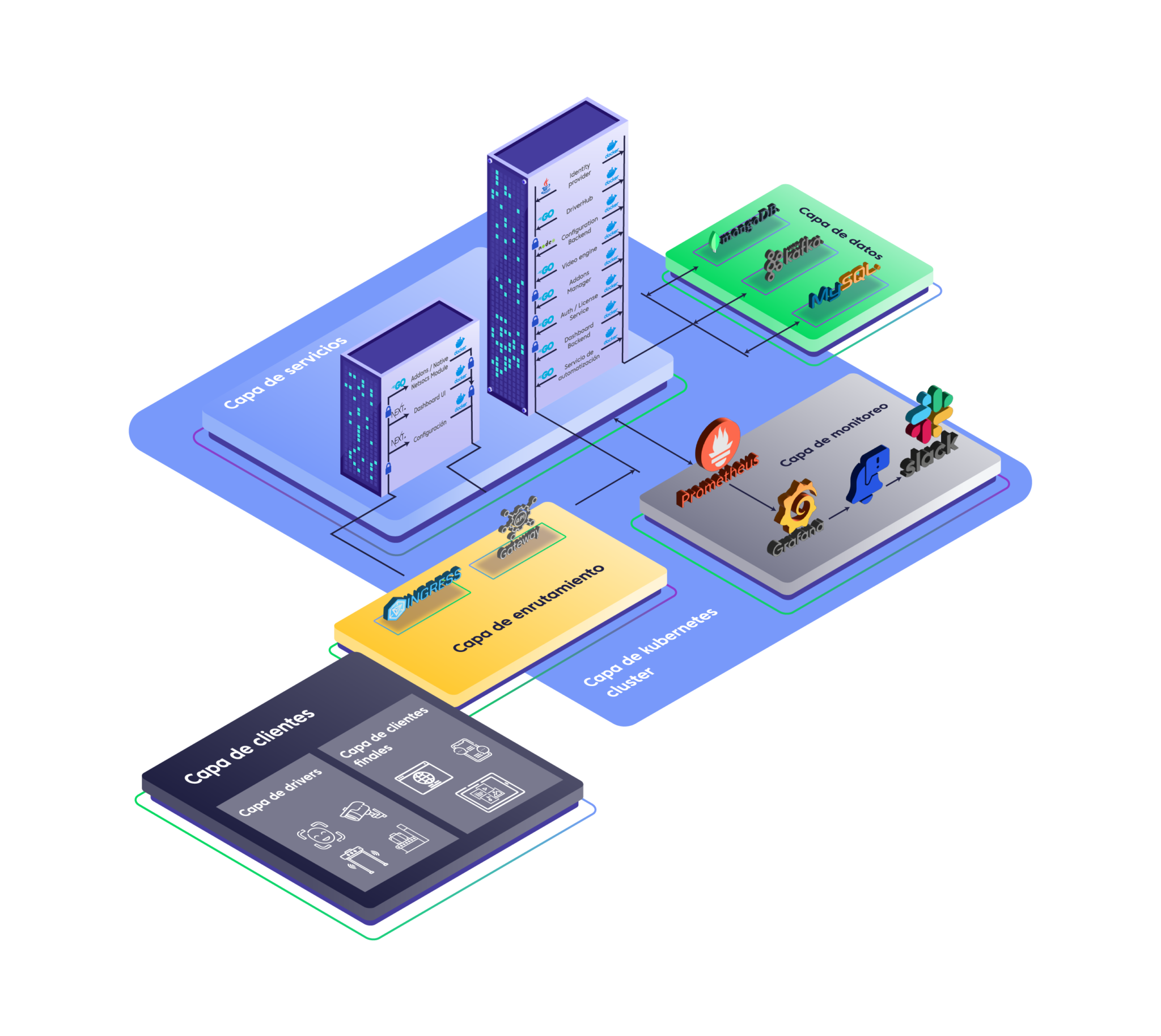
Logical Layer Model¶
The architecture is organized in layers, each with specific responsibilities.
1. Client Layer¶
-
Role:
Entry point for all interactions. Manages connections from human users and field devices. -
Key Components:
- User Applications: Web and mobile clients.
- Devices and Drivers: Hardware integrations, vehicles, and external software.
2. Routing Layer¶
-
Role:
Traffic controller. Manages incoming requests and distributes them to the corresponding microservice. -
Key Components:
- NGINX Ingress Controller:
Load balancing and advanced routing to ensure efficient communication.
3. Service Layer¶
-
Role:
Logical core of the platform based on microservices. Each business function is independent. -
Key Components:
Services for: UsersAutomationAnalyticsIntegrationsEvent Log
This enables functions to be developed, updated, and scaled independently.
4. Data Layer¶
-
Role:
Manages data persistence through a polyglot persistence approach, using the appropriate technology for each type of information. -
Key Components:
| Technology | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| MongoDB | Flexible / unstructured data | Dynamic configurations, detailed logs. |
| MySQL | Transactional / structured data | User profiles, critical records. |
| Redis | In-memory cache | Improves performance and manages message queues. |
5. Monitoring Layer¶
-
Role:
Provides complete observability of platform health and performance. Enables proactive problem detection. -
Key Components:
- Prometheus: Collects performance metrics from microservices and infrastructure.
- Grafana: Visualizes metrics in technical dashboards.
- Slack: Automated alert channel for operations team.
6. Orchestration Layer¶
-
Role:
Foundation of the system. Orchestrates the lifecycle of microservices. -
Key Components:
- Kubernetes (K8s): Automatically deploys, scales, and manages containers.
TIP
Kubernetes allows scaling resources during load spikes and recovering from failures without service interruption.
Architectural Principles¶
This layered design offers key benefits:
- Intelligent Scalability: Independent growth of each microservice according to demand.
- High Availability: Isolated failures don't affect the entire system.
- Development Agility: New features and updates without the need to redesign the entire platform.
- Observability and Proactivity: Integrated monitoring to detect issues before they impact the user.